Cardiovascular diseases
How to Know If You Have AFib: Key Symptoms and Why Monitoring Matters


Key Takeaways
Five million U.S. adults are currently living with AFib, a number expected to grow to 12 million by 2030.
AFib can develop due to medical or lifestyle habits, including high blood pressure (hypertension)
People can experience some or no AFib symptoms, with fatigue being the most common symptom.
Women can also experience additional AFib symptoms, including nausea, shortness of breath, and upper body pain.
Untreated AFib can lead to more frequent and more intense episodes, which increase the risk of heart failure, heart attack and stroke.
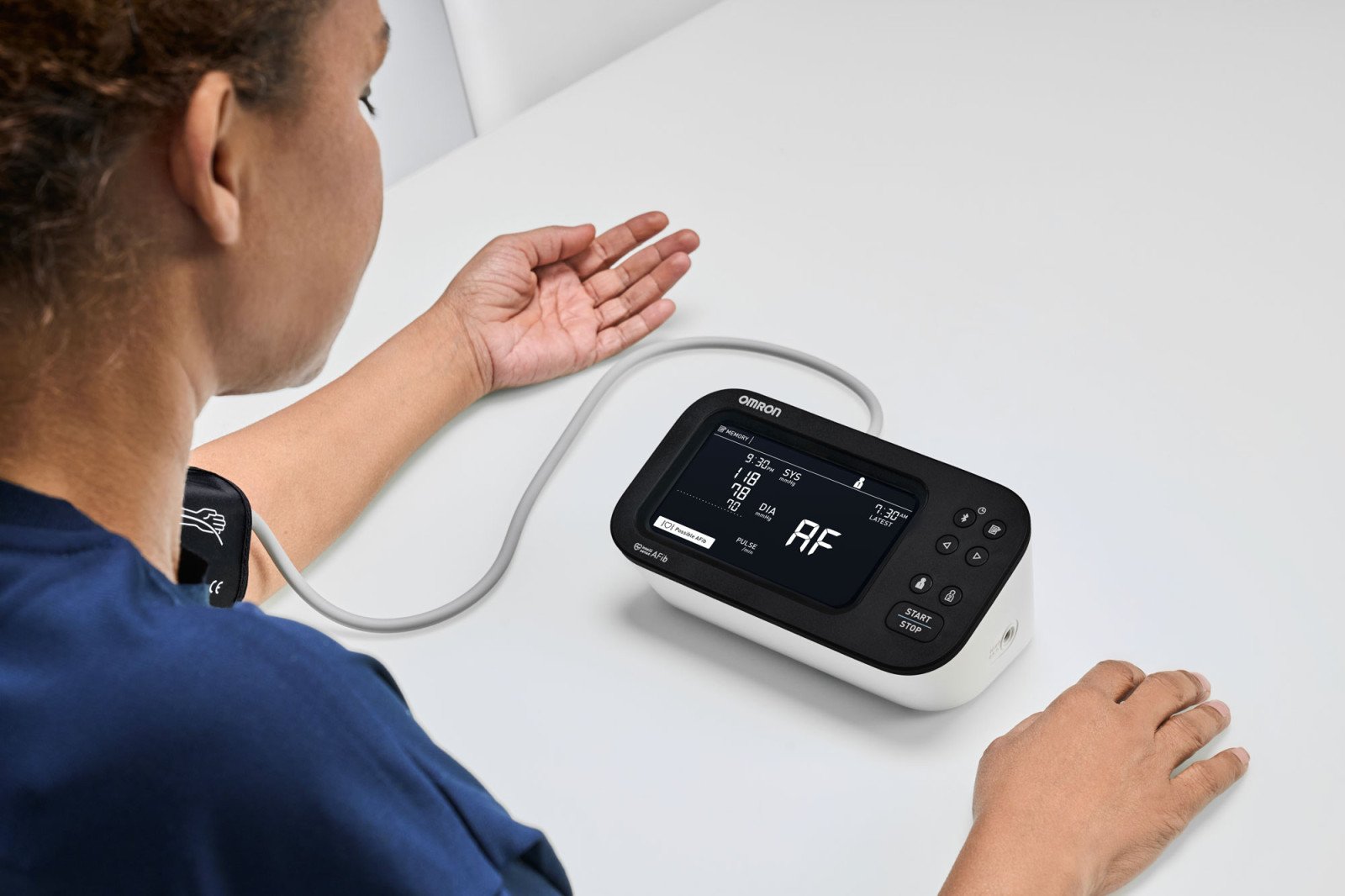
Recognizing the emerging AFib health issue in the U.S., OMRON released four new home blood pressure monitors with Advanced AFib Detection Technology that screen for both in one device. Given the fleeting nature of AFib’s symptoms, this is a big step forward in AFib innovation and detection.
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is a rising health concern in the United States. In February 2025, the American Medical Association reported that more than five million U.S. adults are living with AFib and more than 12 million adults are projected to have the condition by 20301. This is a concerning increase in cases and there could be thousands more adults living with AFib that are undiagnosed. With the number of AFib patients rising quickly, the need for education and awareness of this condition are critical.
For over 50 years, OMRON has been a trusted leader in heart health education and awareness. As we continue to witness the growing impact of AFib on individuals, families, and communities, our commitment has never been stronger. We are dedicated to empowering more people to understand their risk and actively monitor for AFib, making critical steps toward reducing the prevalence of heart failure, heart attacks, and stroke across the U.S.
Let’s dive in to learn more about AFib.
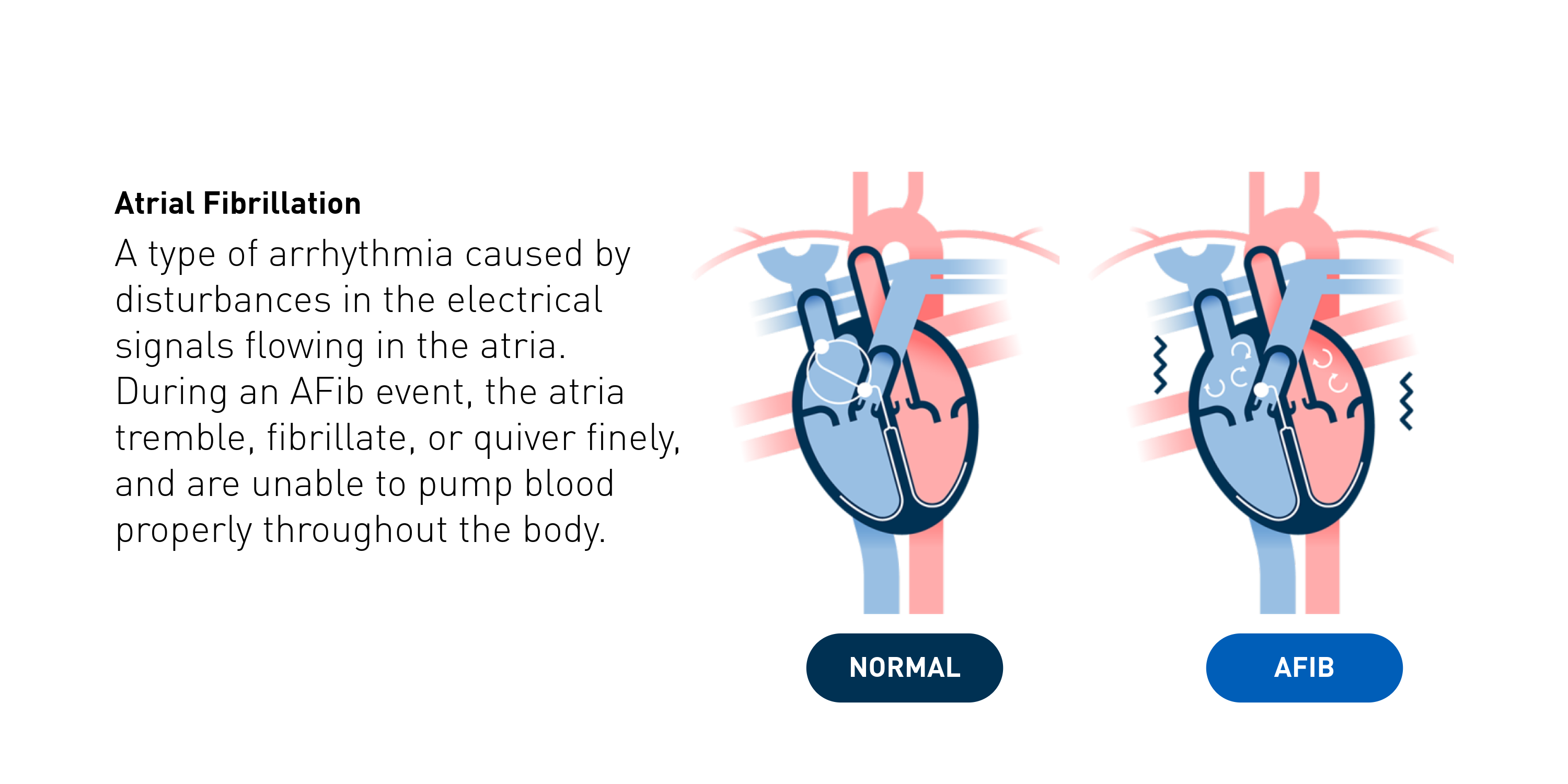
What is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is an irregular heart rhythm that begins in your heart's upper chamber, known as the atria2.
With AFib, your heart’s electrical system doesn’t work as it should. Instead of sending electrical signals in a steady pattern, it sends many different signals at the same time, which is what causes the fast, chaotic rhythm3.
AFib Risk Factors: Medical and Lifestyle
AFib develops when there is damage to the heart’s tissue, which can impact its electrical signaling. Damage to the heart’s tissue and rhythm can develop due to medical and/or lifestyle risk factors. Although AFib can develop at any age, the risk increases more with age, especially in adults over the age of 654.
Below is a detailed look at the medical and lifestyle factors that can increase the risk of developing AFib.
Medical5
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Coronary artery disease
History of heart attack
Sleep apnea
Long-term health conditions, including:
Hyperthyroidism
Type-2 diabetes
Chronic kidney disease
Asthma
Lifestyle6
Smoking
Drinking alcohol
Family history
Sleep apnea
Obesity / weight gain
What is an AFib Event?
An AFib event is when your heart is beating an irregular rhythm. It can feel like a flutter, quiver, or palpitation in your chest7. An AFib event can last for minutes, hours, days, or much longer8.
AFib increases the risk of stroke and heart attack, so it’s important to know symptoms of both to identify if you’re having an AFib episode or one of these more serious cardiac events.
Stroke Symptoms9
Dizziness, balance issues, or problems walking
A headache for no reason
Vision issues in one or both eyes
Numbness or weakness on one side of the body
Trouble talking or understanding other people
Heart Attack Symptoms10
Chest pain, pressure or discomfort in the middle of your chest or upper belly area
Fullness, squeezing, heartburn, other types of indigestion, or a pain running through your left arm
Additional Heart Attack Symptoms for Women11
Shoulder, jaw, or back pain
Shortness of breath
Feeling more tired than normal
Nausea and vomiting
AFib’s Most Common Symptoms
One of the most concerning and frustrating things about AFib is that its symptoms can be fleeting and thus, it can be difficult to diagnose only in a doctor’s office.
Some AFib patients have no symptoms and their diagnosis is only found with a physical exam, while others may have one or more noticeable symptoms. The fleeting nature of AFib makes it tricky to catch without regular monitoring at home.
The most common AFib symptoms in men and women include12:
General tiredness (fatigue)
Rapid and irregular heartbeat
Fluttering or “thumping” in the chest
Dizziness
Shortness of breath and anxiety
Weakness
Faintness or confusion
Fatigue when exercising
Sweating
Chest pain or pressure
AFib Symptoms in Men and Women
While both men and women can experience the AFib symptoms listed above, the condition may sometimes affect women differently13.
Women may also experience14:
A faster heart rate
Increased fatigue and trouble sleeping
Longer episodes of heart fluttering
Generalized weakness
A higher risk of more severe strokes, which are often associated with AFib
What Happens if AFib is Left Unchecked and Untreated?
AFib is a serious condition but it can be managed with treatment. Talking to your care team about your risk factors, family history, and lifestyle will help identify the best treatment options for you.
But what if AFib is left unchecked and untreated?
AFib can start out somewhat benign and infrequent, occurring only for a few minutes or once a week. Over time, however, it can progress and become much more intrusive, lasting for weeks at a time and affecting quality of life15.
Living with AFib automatically increases the risk for serious cardiac events, specifically heart attack and stroke16. That risk increases even more if AFib is undiagnosed and not treated with any medical intervention17. This is why early diagnosis, routine heart health monitoring, and treatment are essential in improving long-term outcomes.
Monitoring for AFib at Home with OMRON
AFib is best diagnosed through an EKG reading. But, given the fleeting and inconsistent nature of AFib episodes, it may not be detected during appointments with your care team.
How can you monitor your heart health when you’re not meeting with your care team?
In 2025, OMRON released four new home blood pressure monitors with Advanced AFib Screening Technology. These monitors automatically screen for AFib during every routine blood pressure reading - no additional steps needed. Each monitor syncs with the OMRON connect app, which can store your readings to share with your doctor, who will help determine your next course of action.
 Learn more about AFib and OMRON’s newest blood pressure monitors with Advanced AFib Screening Technology.
Learn more about AFib and OMRON’s newest blood pressure monitors with Advanced AFib Screening Technology.
References
1,16,17.Berg. (2025). What doctors wish patients knew about atrial fibrillation. American Medical Association. https://www.ama-assn.org/delivering-care/population-care/what-doctors-wish-patients-knew-about-atrial-fibrillation
2,7.(Accessed August 2025). Atrial Fibrillation (AFib). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16765-atrial-fibrillation-afib
3.Mayo Clinic Staff. (2024). Atrial Fibrillation. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atrial-fibrillation/symptoms-causes/syc-20350624
4.(Accessed August 2025). Atrial Fibrillation - Causes and Risk Factors. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/atrial-fibrillation/causes
5,6.(Accessed August 2025). Who is at Risk for Atrial Fibrillation. American Heart Association. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/atrial-fibrillation/who-is-at-risk-for-atrial-fibrillation-af-or-afib#
8.(Accessed August 2025). Duration of Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Stroke. Harvard Medical School. https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/duration-of-atrial-fibrillation-and-risk-of-stroke#
9,10,11.Dumain. (2025). How to Stop an AFib Episode. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/atrial-fibrillation/how-stop-afib-episode
12.(Accessed August 2025). What are the Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation? American Heart Association. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/atrial-fibrillation/what-are-the-symptoms-of-atrial-fibrillation-afib-or-af
13.Miller. (2022). Atrial Fibrillation: The Difference Between Men and Women. HealthGrades. https://resources.healthgrades.com/right-care/atrial-fibrillation/atrial-fibrillation-the-difference-between-men-and-women#
14.Henry Ford Health Staff. (2024). AFib Looks Different in Women. Henry Ford Health. https://www.henryford.com/blog/2024/10/afib-in-women
15.(Accessed August 2025). How Atrial Fibrillation Progresses. StopAFib.org. https://www.stopafib.org/learn-about-afib/what-is-afib/how-afib-progresses/